Document Type
Emerging StandardPublished date
05/15/2023Input Close Date
To be determinedScientific Experts
Dom Vicchio (Sr. Director, USP)
Introduction
To jump‐start the standard development process and have earlier stakeholder engagement, USP is piloting a new approach for developing and sharing information with our stakeholders. Through a collaboration between USP’s Small Molecules Department and the Global Analytical Development Laboratory, methods will be developed and validated for drug substances and drug products for which no monographs are currently available. The Emerging Standards are intended to improve USP’s official standards elaboration process by increasing transparency and allowing for broader stakeholder participation by publishing on the USP website prior to formal notice and comment through publication in the Pharmacopeial Forum.
Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets have been evaluated and shown to be a suitable candidate for development under this new program. The methods in this document are being published to help analyze Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets as a part of USP’s mission to improve global health through public standards that help ensure the safety, quality, and benefit of medicines and foods.
Certain commercial equipment, instruments, or materials may be identified in this document to specify adequately the experimental procedure. Such identification does not imply approval, endorsement, or certification by USP of a particular brand or product, nor does it imply that the equipment, instrument, or material is necessarily the best available for the purpose or that any other brand or product was judged to be unsatisfactory or inadequate.
This document is not a USP compendial standard and is intended to serve as a resource for information purposes only. It does not reflect USP or USP’s Expert Body opinions of future revisions to the official text of the USP‐NF. Parties relying on the information in this document bear independent responsibility for awareness of, and compliance with, any applicable federal, state, or local laws and requirements.
Background
Pregabalin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Pregabalin is the active ingredient in Pregabalin Oral Solution and Tablets. It works by decreasing the number of pain signals that are sent out by damaged nerves in the body. Pregabalin is also used to relieve neuropathic pain that can occur after a spinal cord injury, treat fibromyalgia, and if used along with other medications to treat certain types of seizures.1
The USP‐NF has a drug substance monograph for Pregabalin but does not contain a drug product monograph for Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets. It was decided that USP should consider developing methods for Pregabalin drug products as part of the emerging standards initiative. The HPLC‐UV methods developed and validated for the Pregabalin Oral Solution were adopted for the Organic Impurities and Assay procedures of Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets in support of the USP Emerging Standards initiative. However, due to differences in sample matrices, some minor changes were made to the chromatographic conditions to account for a late eluting excipient (povidone) peak and the diluent was changed to sodium sulfate anhydrous (0.5M) in 0.1% phosphoric acid in water to aid in sample extraction. With the minor adoptions, no additional degradation or robustness study was performed. For information related to the degradation or robustness studies, please refer to our Pregabalin Oral Solution article on this website.
This document describes methods and includes supporting chromatographic systems data for peak retention time match, which may be suitable for identifying pregabalin in the presence of various impurities and excipients. High‐performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods and supporting validation data, which may be suitable for determining strength and purity, are also described.
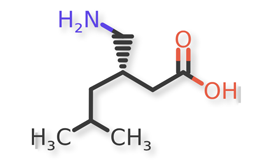
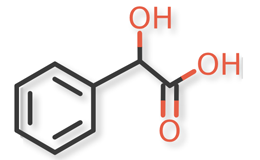
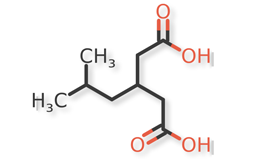
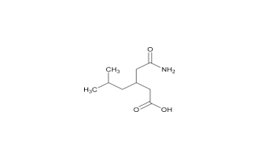
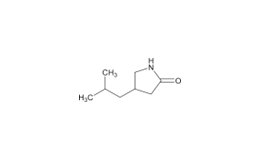
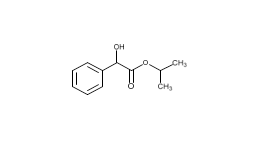
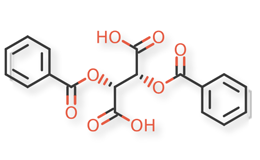
Pregabalin and related compounds are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
EXPERIMENTAL
Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets and related compounds (isobutylglutaric acid, isobutylglutarmonoamide, isopropyl mandelate, and dibenzoyl‐L‐tartaric acid) were procured from different suppliers. USP Reference Standards were available for pregabalin, pregabalin related compound C, and mandelic acid.
Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets from three commercial sources were used to evaluate identification by ultraviolet (UV) spectral match and retention time match, assay, and organic impurities using methods described in this document.
IDENTIFICATION
Identification (ID) of pregabalin in Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets was evaluated using HPLC‐UV with (PDA) detector and chromatographic HPLC retention time match. However, since UV spectrum of pregabalin does not contain any maximum at the wavelengths above 200 nm, the ID by spectral match, as obtained in Assay, may not be suitable but is shown below for information only.
A. HPLC‐UV with PDA Detector:
The HPLC assay procedure with PDA detector was used as the chromatographic identification procedure. See the Assay section for the method conditions and solution preparations. The validation parameter and results are summarized in Table 1 and UV spectra of the pregabalin standard, and sample are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
| Parameter | Samples and Procedure | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral Agreement | Collect PDA data from 190–400nm for the Standard solution and Sample solution | The UV spectrum of the pregabalin peak from the Sample solution matched the spectrum of pregabalin in the Standard solution and exhibited maximum only at the same wavelength (198 nm) as the Standard solution. No maxima and minima (>200 nm) were exhibited; ID by UV spectral match may not be suitable. |
| Abbreviation: PDA, Photodiode array; UV, ultraviolet | ||
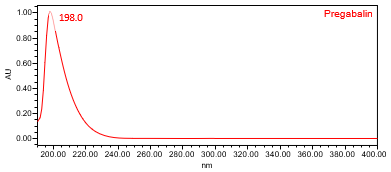
B. Retention Time Match:
The chromatographic retention time is used as an identification method. The HPLC assay procedure was utilized for this identification test. Refer to the Assay section for the method conditions and solution preparations.
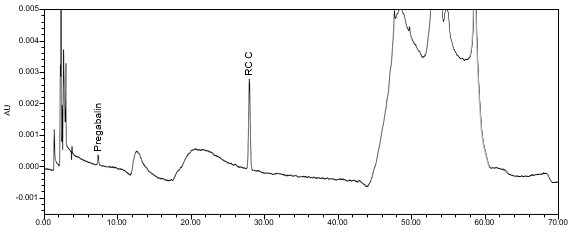
The validation parameter and results are summarized in Table 2, and the example chromatograms for the Standard solution and Sample solution are shown in Figures 5 and 6, respectively.
| Parameter | Samples | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Retention Time Match | Standard solution and Sample solution | The relative standard deviation (%RSD) of the pregabalin peak retention time for all injections of the Standard solution and Sample solution was <1.0%. |
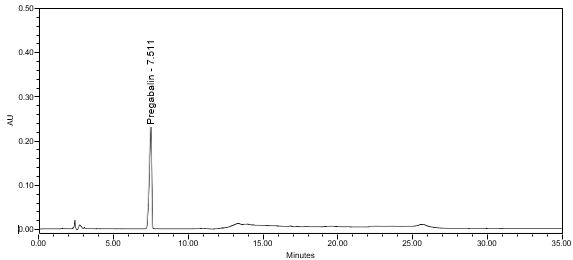
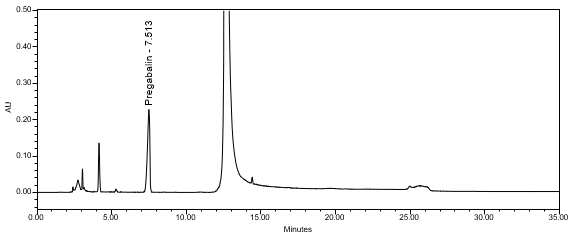
ASSAY
A gradient reversed‐phase HPLC procedure was developed for the assay and organic impurity analyses of Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets. The procedure was validated using the criteria described in USP General Chapter <1225>, Validation of Compendial Procedures2 and found to be specific, linear, accurate, precise, robust, and free from interference for the samples evaluated.
Chemicals:
Ammonium phosphate dibasic (HPLC grade), sodium sulfate, anhydrous, 99+% (HPLC grade) were obtained from Acros Organics. Optima LC/MS grade acetonitrile and methanol, and HPLC grade orthophosphoric acid were obtained from Fisher Scientific. Ultrapure water used for HPLC analysis was obtained from a Milli‐Q water purification system.
Instruments and method:
The analysis of pregabalin was performed using Waters Alliance e2695 with 2998 PDA detector and Agilent 1260 Infinity II with G4212‐60008 DAD detector, and the results were processed by Empower (Waters software). The GL Sciences Inertsil ODS‐3V C18, 4.6‐mm x 25.0‐cm, 5 µm column was used for analysis. The analysis was performed at 50°C, with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min and 80 µL as the injection volume. Autosampler temperature was kept at ambient. The PDA detector was set at 190‐400 nm wavelength and the detection of chromatogram was at 215 nm. Separation was achieved by a gradient program as listed in Table 3.
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (%) | Mobile phase B (%) | Mobile phase C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
| 7 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
| 10 | 40 | 16 | 44 |
| 22 | 40 | 16 | 44 |
| 23 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
| 35 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
Solutions:
Mobile phase A: Weigh and transfer about 10.56 g of ammonium phosphate dibasic into 2 L of water. Adjust to pH 6.50 ± 0.05 with orthophosphoric acid. Filter the solution through a 0.2‐µm membrane filter.
Mobile phase B: Methanol.
Mobile phase C: Acetonitrile.
Diluent: 0.5M Sodium sulfate anhydrous in 0.1% phosphoric acid in water.
Preparation of Isobutylglutaric acid stock solution:
Isobutylglutaric acid stock solution consisting of 0.10 mg/mL was prepared by dissolving the appropriate amount of impurity in Diluent with the aid of sonication.
Preparation of System suitability solution:
A solution consisting of 2.5 mg/mL of Pregabalin standard and 0.010 mg/mL of Isobutylglutaric acid was prepared by combining appropriate amount of Pregabalin standard with appropriate volume of Isobutylglutaric acid stock solution in Diluent. Sonicated to dissolved.
Preparation of Standard solution:
Standard solution containing 2.5 mg/mL of pregabalin standard was prepared using Diluent.
Preparation of Sample solution:
Nominally 2.5 mg/mL of pregabalin from Pregabalin ER Tablets was prepared as follows. Accurately weigh and transfer an amount of Pregabalin ER Tablets composite (finely ground NLT 20 tablets), equivalent to 25 mg of pregabalin, into a 20‐mL volumetric flask. Pipet in 10.0 mL of Diluent, swirl to disperse. Add magnetic stir bar, cap, and stir for 60 min. Intermittently swirl solution to keep sample from sticking to side of flask. Take an aliquot of sample solution and centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min, then take clear solution (middle layer) for HPLC injection.
Analytical parameters and validation:
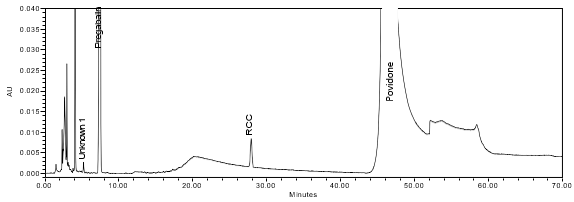
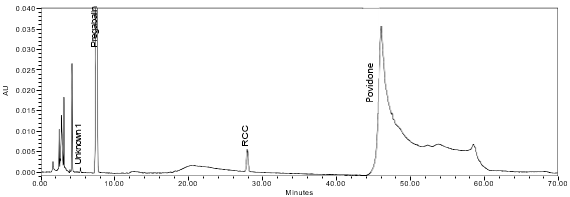
The optimized chromatographic conditions were validated by evaluating specificity, linearity, precision, and accuracy as described in <1225>2. The system suitability requirements are summarized in Table 4. The validation parameters, solutions, and results for Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets are summarized in Table 5. The example chromatograms for the assay Standard solution and Sample solution are shown in Figures 5 and 6, respectively.
| Parameter | Solutions | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Retention time | Standard solution | About 7.5 min |
| Tailing factor | Standard solution | Tailing was NMT 2.0 |
| System Precision (for 5 replicate injections) | Standard solution | %RSD was NMT 0.5 |
| Resolution | System suitability solution | NLT 1.5 |
| Abbreviation: RSD, relative standard deviation; NMT, not more than; NLT, not less than | ||
| Parameter | Solutions | Results |
|---|---|---|
Specificity (Chromatographic Separation)
Peak Purity Analysis (Spectral Homogeneity) | Diluent, Standard solution, and Sample solution | Any impurity peak from the Standard solution and Sample solution was separated from the pregabalin peak by a resolution ≥1.5. The PDA data from 200–240 nm showed homogeneity of UV spectrum for the pregabalin peak, indicating the lack of coelution. |
| Identification | Standard solution and Sample solution | The RSD for pregabalin peak retention time from all injections of Standard solution and Sample solutions is NMT 1.0% |
| Linearity | Linearity solutions from 50% to 150% of the nominal concentration (1.25, 1.88, 2.5, 3.13, and 3.75 mg/mL of pregabalin) | The correlation coefficient (r) was not less than 0.999. The bias of the linearity curve due to the intercept not being zero was less than ± 2.0%. |
| Accuracy | Accuracy solutions from 110–130% of the nominal concentration were prepared in triplicate: 110% (2.75 mg/mL), n=3 120% (3.0 mg/mL), n=3 130% (3.25 mg/mL), n=3 | The average recovery at each level was within 100 ± 3.0%. |
| Repeatability | Repeatability solutions: 6 Sample solutions | The %RSD was NMT 2.0 (n=6). |
| Intermediate Precision | Intermediate precision was done by a different analyst, on a different day by using a different instrument and different column lot number. | The %RSD was NMT 2.0 (n=6). The %RSD was NMT 3.0 for the combined data of the first and second analysts (n=12). |
| Solution Stability | Standard solution and Sample solution | Standard solution and Sample solution were stable for 24 hours at ambient temperature. |
| Sample Assay Test | Sample solution | Sample 1: 96.6% (n=12) Sample 2: 97.3% (n=2) Sample 3: 97.0% (n=2) |
ORGANIC IMPURITIES
The HPLC method used for the analysis of the organic impurities is the same procedure as described in the Assay section, with only modification to the HPLC gradient program summarized in Table 6. The method can be used to quantitate degradants in Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets. The procedure was validated using the criteria described in <1225>2 and found to be specific, accurate, precise, robust, linear, and free from interference for the samples evaluated. The validation study showed that the method was suitable for evaluation of the organic impurities in Pregabalin Extended‐Release Tablets drug product. It should be noted that when working with the GL Sciences Inertsil column, daily column wash (approximately every 24 hours) is recommended due to possible excipient interference and column buildup of retained materials, requiring strong organic elution.
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (%) | Mobile phase B (%) | Mobile phase C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
| 7 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
| 16 | 64 | 18 | 18 |
| 40 | 64 | 18 | 18 |
| 45 | 42 | 18 | 40 |
| 55 | 42 | 18 | 40 |
| 56 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
| 70 | 82 | 16 | 2 |
Solutions:
Prepare Mobile phase A, Mobile phase B, Mobile phase C, System suitability solution, and Diluent and follow chromatographic conditions per the assay procedure with gradient program in Table 6.
Preparation of Standard stock solution 1:
Standard stock solution 1 (0.1 mg/mL) was prepared by dissolving an appropriate amount of Pregabalin standard and pregabalin related compound C standard in Diluent.
Preparation of Standard stock solution 2:
Standard stock solution 2, containing 0.025 mg/mL each of Pregabalin standard and pregabalin related compound C standard, was prepared from the Standard stock solution 1 by further diluting with the Diluent.
Preparation of Standard solution:
Standard solution, containing 0.005 mg/mL each of Pregabalin standard and pregabalin related compound C standard, was prepared from the Standard stock solution 2 by further diluting with the Diluent.
Sensitivity solution:
Sensitivity solution, containing 0.0025 mg/mL each of Pregabalin standard and pregabalin related compound C standard, was prepared from the Standard stock solution 2 by further diluting with the Diluent.
Preparation of Sample solution:
Nominally 2.5 mg/mL of pregabalin from Pregabalin ER Tablets is prepared as follows. Accurately weigh and transfer an amount of Pregabalin ER tablets composite (finely ground NLT 20 tablets), equivalent to 25 mg of pregabalin, into a 20‐mL volumetric flask. Pipet in 10.0 mL of Diluent, swirl to disperse. Add magnetic stir bar, cap, and stir for 60 min. Intermittently swirl solution to keep sample from sticking to side of flask. Take an aliquot of sample solution and centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min, then take clear solution (middle layer) for HPLC injection.
Analytical parameters and validation:
The optimized chromatographic conditions were validated by evaluating specificity, linearity, accuracy, repeatability, intermediate precision as described in USP General Chapter <1225>.2 Linearity was established for pregabalin and pregabalin related compound C, whereas accuracy and repeatability were established for pregabalin related compound C.
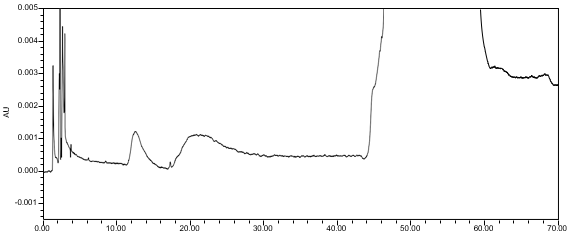
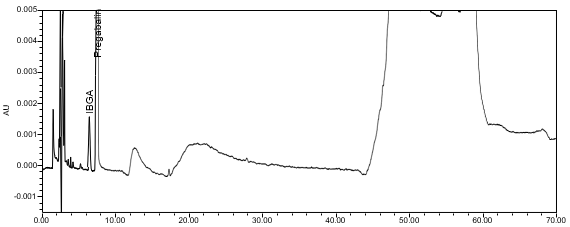
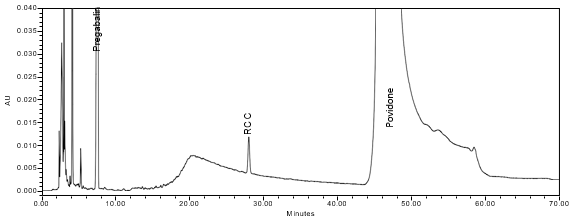
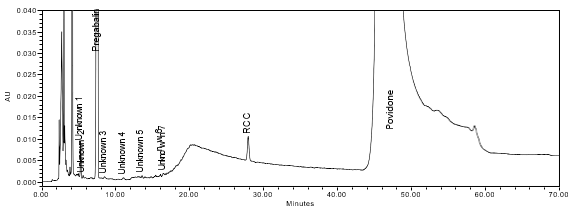
The limit of quantitation (LOQ) was established at 0.10% of sample concentration. The system suitability requirements are summarized in Table 7. The validation parameters and testing results for Pregabalin ER Tablets are summarized in Table 8. The example chromatograms of Diluent, Sensitivity solution, System suitability solution, Sample solution and Sample solution with spiked pregabalin related compound C (LOQ), are presented in Figures 7–11, respectively.
| Parameter | Solution | Results |
|---|---|---|
USP Signal‐to‐Noise Ratio Pregabalin | Sensitivity solution | (See Figure 8) NLT 10 |
Resolution Minimum resolution between pregabalin and isobutylglutaric acid | System suitability solution | (See Figure 9) NLT 3.1 |
Relative Retention Time(s) Pregabalin | Standard solution | 1.0 3.8 |
System Precision Pregabalin | Standard solution | 3.5% 1.4% |
| Parameter | Solutions | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Specificity | Blank (Diluent), Sample solutions, and Spiked solutions | No interference between peaks of interest. Any impurity peak ≥0.1% total area was separated from the pregabalin and pregabalin related compound C peaks by a resolution of ≥1.5. |
Linearity Pregabalin | Linearity solutions from LOQ (0.1%) to 0.7% of the nominal concentration (2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 12.5, and 17.5 µg/mL) in Diluent | The correlation coefficient of the linear curves for pregabalin and pregabalin related compound C were not less than 0.99. |
| Relative Response Factor (RRF) Values | Linearity solutions From LOQ (0.1%) to 0.7% of the nominal concentration of pregabalin and pregabalin related compound C in Diluent | For results, refer to Table 9. |
Accuracy Pregabalin Related Compound C | Accuracy solutions: pregabalin related compound C spiked in Sample solution at 3 levels: LOQ (0.1%): n=6 | The average recovery for pregabalin related compound C at each level were: 0.1%: 87.6% |
Repeatability Pregabalin Related Compound C | Repeatability solutions: 6 spiked Sample solutions at the LOQ level | The %RSD of the recovery was 4.0% (n=6). See Figure 10 for example chromatogram. |
Intermediate Precision Pregabalin Related Compound C | Repeatability solutions: 6 spiked Sample solutions at the LOQ level prepared and evaluated by a different analyst on a different day, using a different instrument and different column lot number | The average recovery at LOQ was 88.9%. RSD of the 6 results at LOQ was 4.3%. RSD of the 12 results (analyst 1 and 2) at LOQ was 4.0%. |
| Sample Analysis | Sample solution | See Figure 11. |
Solution Stability Pregabalin | Sensitivity solution and spiked Sample solution at LOQ level. Freshly prepared samples analyzed (t=0) periodically for about 24 hours at ambient temperature. | Peak area changes of pregabalin (in Sensitivity solution only) and pregabalin related compound C peaks (in both solutions) were within ±10% from the initial time point. |
| Impurity Name | RRF |
|---|---|
| Pregabalin related compound C | 17.16 |
| Pregabalin | 1.00 |
RRF value of pregabalin related compound C was calculated by dividing the slope of the linearity curve for pregabalin related compound C by the slope of the linearity curve for pregabalin.
Comment Not Found