Document Type
Emerging StandardPublished date
05/01/2022Input Close Date
To be determinedScientific Experts
Mark Tiedje (Sr. Scientist II, USP)
Introduction
A lack of donations has resulted in the inability of USP to develop documentary standards that meet customer needs. In order to jump-start the standard development process and have earlier stakeholder engagement, USP is piloting a new approach to develop and share information with our stakeholders. Through a collaboration between USP’s Small Molecules department and the Global Analytical Development Laboratory, methods will be developed and validated for drug substances and drug products for which no monographs are currently available. These methods and data will be published on the USP website for stakeholder input.
Acetaminophen Injection has been evaluated and shown to be a suitable candidate for development under this new program. The methods for analyzing Acetaminophen Injection are being published as part of USP’s mission to improve global health through public standards that help ensure the safety, quality, and efficacy of medicines and foods.
Where a particular brand or source of a material, instrument, piece of equipment, or manufacturer or distributor is mentioned, this identification is furnished solely for informational purposes as a matter of convenience, without implication of approval, endorsement, or certification.
This document is not a USP compendial standard and is intended to serve as a resource for informational purposes only. It does not reflect USP or USP’s Expert Body opinions of future revisions to the official text of the USP–NF. Parties relying on the information in this document bear independent responsibility for awareness of, and compliance with, any applicable federal, state, or local laws and requirements.
Background
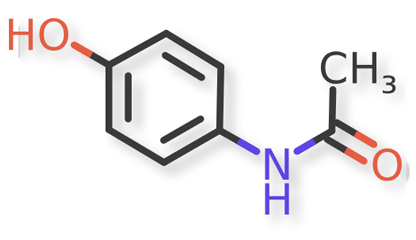
Acetaminophen or Paracetamol, acetamide, N-(4-hydroxyphenyl), is the active ingredient in Acetaminophen Injection, a clear solution supplied in sterile and nonpyrogenic formulation. Acetaminophen Injection is a non-salicylate antipyretic and non-opioid analgesic agent that is administered via intravenous infusion. The mechanism of the analgesic and antipyretic properties of acetaminophen has not been established, but it is thought that the antipyretic activity may result from inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. The in vivo effects of acetaminophen are similar to those of selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors1.
Acetaminophen is widely used in nonprescription and antipyretic medication for mild-to-moderate pain and fever or as an opioid adjunct for moderate-to-severe pain management. Harmless at low doses, acetaminophen has a direct hepatotoxic potential when taken in high doses and can cause acute liver injury and death from acute liver failure2. The USP–NF contains a drug substance monograph for Acetaminophen and a number of drug product monographs that cover various dosage formulations containing acetaminophen. The methods described in this document were developed because there is no monograph for Acetaminophen Injection.
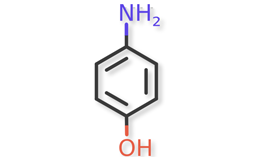
Methods and supporting data are described for peak retention time match and photodiode array spectral match from the chromatographic system that is suitable for establishing the identification of acetaminophen in the presence of various impurities. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods and supporting validation data suitable for determining the strength and purity are also described. Furthermore, 4-Aminophenol, the main degradation product of acetaminophen, was analyzed using both the impurities method in this document and the procedure from general chapter 4-Aminophenol in Acetaminophen Containing Drug Products <227>3.
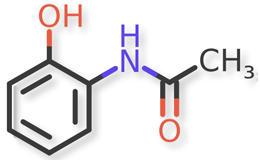
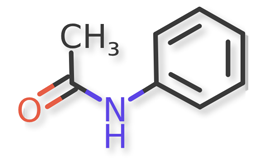
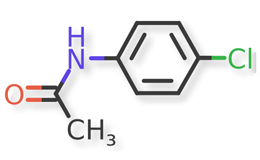
Acetaminophen and known acetaminophen impurities are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2a, Figure 2b, Figure 2c, Figure 2d, Figure 2e, Figure 2f, respectively. Related compound (RC) B, RC C, RC D, and RC J and acetaminophen dimer impurity are used to refer to these known impurities throughout this article.
EXPERIMENTAL
Materials: Reference standards (RS) for Acetaminophen, Acetaminophen Related Compound B, Acetaminophen Related Compound C, Acetaminophen Related Compound D, Acetaminophen Related Compound J, and 4-Aminophenol were provided by USP. The Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity was obtained from SynZeal.
Acetaminophen Injection samples from three commercial sources were used to evaluate the assay and impurity methods described in this article.
Identification:
Identification for acetaminophen in Acetaminophen Injection products was evaluated using HPLC-UV with a photodiode array (PDA) detector and chromatographic HPLC retention time match.
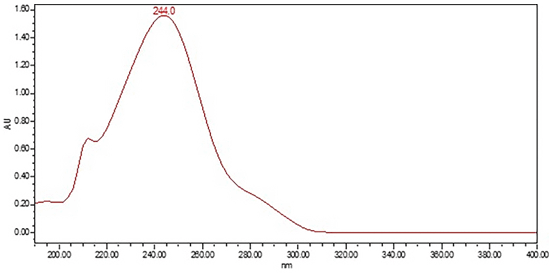
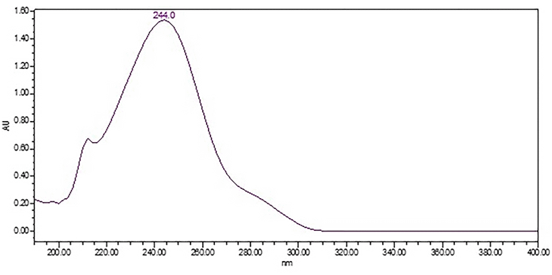
HPLC-UV with PDA Detector: The HPLC Assay procedure with PDA detector was used as the chromatographic identification procedure. See the Assay for the method conditions and preparations of Standard solution and Sample solutions. The validation parameters and results are summarized in Table 1, and representative UV spectra of acetaminophen from the Standard solution and Sample solutions are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
| Parameter | Samples and Procedure | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral agreement | Collect PDAa data from 190 to 400 nm for the Standard solution and Sample solution | The UVb spectrum of the acetaminophen peak from the Sample solution matched the spectrum of acetaminophen in the Standard solution and exhibited maxima and minima only at the same wavelengths as that of the Standard solution |
aPDA, photodiode array detector. bUV, ultraviolet. | ||
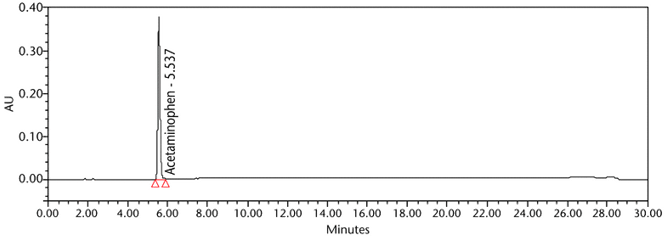
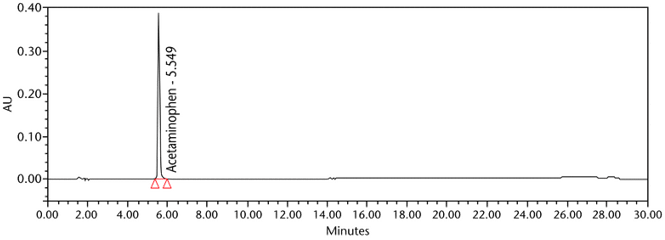
Retention Time Match: The chromatographic peak retention time is used as an alternative identification method. The HPLC Assay procedure was utilized for this identification test. See the Assay for the method conditions and preparations of Standard solution and Sample solutions.
The validation parameter and results are summarized in Table 2, and the example chromatograms for the Standard solution and Sample solution are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively.
| Parameter | Samples | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Retention time match | Standard solution and Sample solution | The relative standard deviation (%RSD) of the acetaminophen peak retention time for all injections of the Standard solution and Sample solution was NMT 1.0%. |
ASSAY
An HPLC method using an X-Bridge C18 column and a mass spectrometric (MS) compatible mobile phase adapted from the Organic Impurities test in the USP Acetaminophen Tablets monograph4 was modified to ensure the separation of potential impurities present in Acetaminophen Injection products. The main objective of the chromatographic method was to separate specified impurities listed in the Acetaminophen monograph from the main peak with sufficient resolution. The procedure was validated based on the criteria described in the general chapter Validation of Compendial Procedures <1225>5 and found to be specific, accurate, precise, robust, and free from interference for the samples evaluated.
Chemicals: Ammonium acetate and methanol were purchased from Merck. Ammonium formate, formic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, and acetonitrile were purchased from Qualigen.
Instruments and method: The chromatographic systems utilized were a Waters Alliance 2695 HPLC and an Agilent/1260-G131B HPLC. The Waters X-Bridge C18, 4.6-mm × 15.0-cm, 3.5-µm column was used for analysis. The flow rate was 0.9 mL/min. The column temperature was maintained at 40° C. The detection was monitored at a wavelength of 272 nm, and the injection volume was 25 µL. The separation was achieved by a gradient program as listed in Table 3.
Solutions
Solution A: A mixture of acetonitrile, methanol, and water in the proportion of 10:75:15 (v/v/v)
Mobile phase A: 40 mM ammonium acetate in water, to which trifluoroacetic acid was added at a ratio of 1.0 mL/L
Mobile phase B: 40 mM ammonium acetate in Solution A, to which trifluoroacetic acid was added at a ratio of 1.0 mL/L
Buffer solution: 30 mM ammonium formate in water, to which formic acid was added at a ratio of 1.0 mL/L
Diluent: A mixture of methanol and Buffer solution in the proportion of 5:95 (v/v)
Preparation of Standard solution: Standard solution containing 0.1 mg/mL of USP Acetaminophen RS was prepared using Diluent
Preparation of Sample solutions: Sample solutions nominally containing 0.1 mg/mL of acetaminophen were prepared by diluting portions of Acetaminophen Injection samples with Diluent
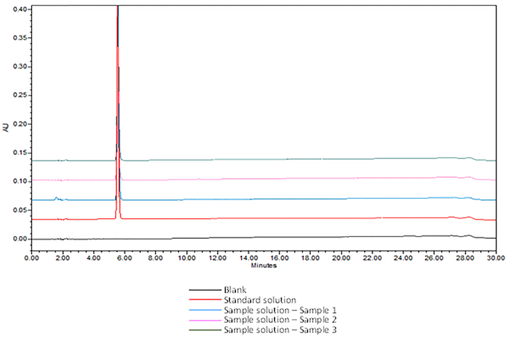
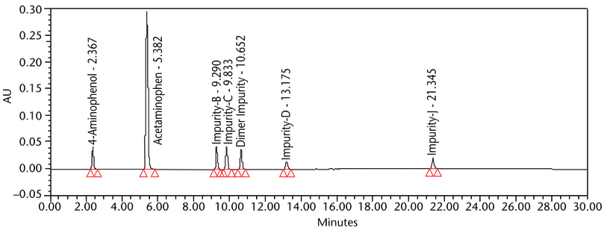
Analytical Parameters and Validation: The optimized chromatographic conditions were checked for robustness and validated by evaluating specificity, linearity, precision, and accuracy as described in <1225>5. The system suitability results are summarized in Table 4. The validation parameters and results for Acetaminophen Injection are summarized in Table 5. The overlay chromatograms of the Diluent, Standard solution, and Sample solution prepared from three different sources are presented in Figure 7. The specificity of the method in the presence of known impurities of acetaminophen is shown in Figure 8.
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (%) | Mobile phase B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 90 | 10 |
| 3 | 90 | 10 |
| 23 | 40 | 60 |
| 25 | 20 | 80 |
| 26 | 90 | 10 |
| 30 | 90 | 10 |
| Parameter | Solutions | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Retention time | Standard solution | About 5.7 min |
| Tailing factor | Standard solution | NMT 2.0 |
| System precision (RSD for 5 replicate injections) | Standard solution | NMT 0.5% |
| Parameter | Solutions | Results |
|---|---|---|
Specificity (chromatographic separation) Peak Purity Analysis (spectral homogeneity) | Blank (Diluent), Standard solution, and Sample solutions | The PDA data from 190 to 400 nm showed homogeneity of the UV spectrum for the acetaminophen peak, indicating the lack of coelution. |
| Linearity | Linearity solutions from 50% to 150% of the nominal concentration (0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.125, and 0.15 mg/mL of acetaminophen) | The correlation coefficient (r) was NLT 0.999. The bias of the linearity curve due to the intercept not being zero was less than ±2.0%. |
| Accuracy | Accuracy solutions from 110%–130% of the nominal concentration were prepared in triplicate. 110% (0.11 mg/mL), n = 3 120% (0.12 mg/mL), n = 3 130% (0.13 mg/mL), n = 3 | The average recovery at each level was within 100% ± 3.0%, calculated against the Standard solution. |
| Repeatability | Repeatability solutions: 6 Sample solutions at the nominal concentration | The %RSD of assay values calculated against the standard solution was NMT 2.0% (n = 6) |
| Intermediate Precision | Repeatability test performed by a different analyst on a different day by using different instrument and using a different serial number of the column | The %RSD of assay values calculated against the Standard solution was NMT 2.0% (n = 6). The %RSD of assay values calculated against the Standard solution was NMT 3.0% for the combined data of the first and second analysts (n = 12). |
| Solution Stability | Standard solution and Sample solutions | Standard solution and Sample solutions were stable for 24 h at room temperature. |
| Sample Assay Test | Sample solutions | 98.0%–103.1% for the three sources tested, calculated against the Standard solution |
ORGANIC IMPURITIES
The HPLC method used for analysis of the organic impurities is the same procedure as described in the Assay. The method can be used for the quantitation of degradants in Acetaminophen Injection drug products including 4-Aminophenol. The procedure was validated based on the criteria described in <1225>5 and found to be specific, accurate, precise, robust, linear, and free from interferences for the samples evaluated. The validation study showed that the method was suitable for evaluation of organic impurities in Acetaminophen Injection products.
Solutions: Diluent, Mobile phase A, and Mobile phase B preparations were based on the Assay procedure.
Preparation of Standard stock solution: A stock solution of USP Acetaminophen RS (0.1 mg/mL) was prepared by dissolving an appropriate amount in Diluent. An aliquot of this solution was further diluted with Diluent to yield a 0.01 mg/mL solution.
Preparation of Impurity solution A: Impurity solution A, consisting of 0.1 mg/mL each of USP 4-Aminophenol RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound B RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound C RS, and Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity, was prepared by dissolving the appropriate amounts of each impurity in a suitable volumetric flask with methanol (about 12% of the final volume) and diluting with Diluent to the final volume.
Preparation of Impurity solution B: Impurity solution B, consisting of 0.1 mg/mL of USP Acetaminophen Related Compound D RS and USP Acetaminophen Related Compound J RS, was prepared by dissolving the appropriate amounts of each impurity in a suitable volumetric flask with methanol (about 12% of the final volume) and diluting with Diluent to the final volume.
Preparation of System suitability solution: A solution consisting of 1.0 mg/mL of USP Acetaminophen RS, and 1.5 μg/mL (0.15%) each of USP 4-Aminophenol RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound B RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound C RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound D RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound J, and Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity was prepared by combining an appropriate amount of USP Acetaminophen RS with appropriate quantities of Impurity solution A and Impurity solution B in Diluent.
Preparation of Sensitivity solution: A solution consisting of 0.3 μg/mL (0.03%) each of USP Acetaminophen RS, USP 4-Aminophenol RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound B RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound C RS, Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity, and 0.5 μg/mL (0.05%) each of USP Acetaminophen Related Compound D RS and USP Acetaminophen Related Compound J RS was prepared by diluting appropriate quantities of Standard stock solution, Impurity solution A, and Impurity solution B with the appropriate amount of Diluent.
Preparation of Standard solution: The Standard solution, consisting of 1.5 μg/mL (0.15%) each of USP Acetaminophen RS, USP 4Aminophenol RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound B RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound C RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound D RS, USP Acetaminophen Related Compound J RS, and Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity, was prepared by diluting appropriate quantities of Standard stock solution, Impurity solution A, and Impurity solution B with the appropriate amount of Diluent.
Preparation of Sample solutions: Sample solutions nominally containing 1.0 mg/mL of acetaminophen were prepared by diluting a portion of acetaminophen injection with Diluent.
Analytical parameters and validation: The optimized chromatographic conditions were checked for robustness and validated by evaluating specificity, linearity, accuracy, repeatability, and intermediate precision as described in <1225>5. Linearity was established for acetaminophen and related impurities, whereas accuracy and repeatability were established for acetaminophen related impurities.
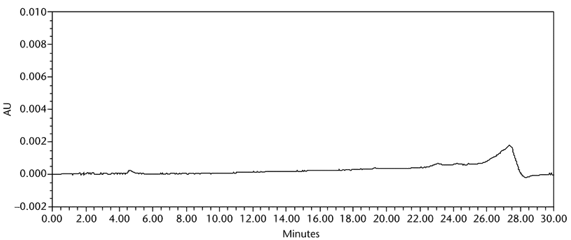
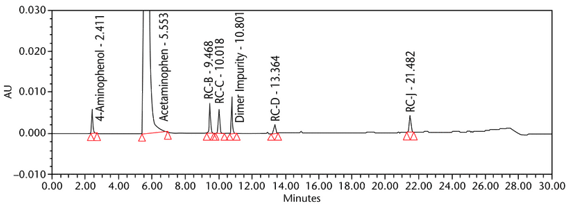
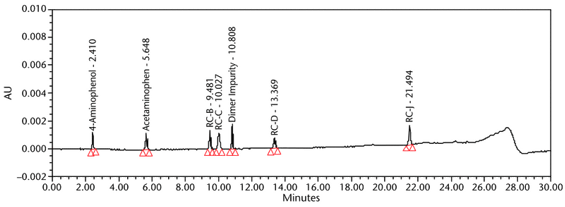
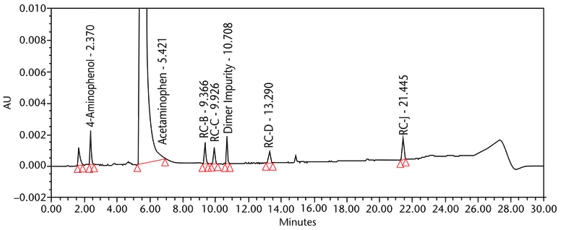
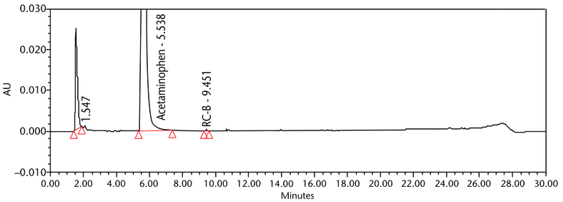
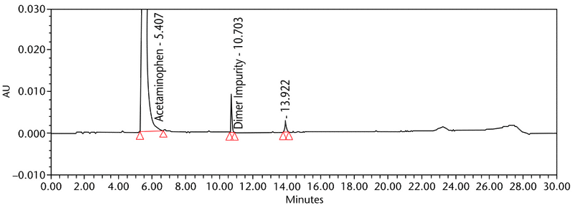
The limit of quantitation (LOQ) was established experimentally to the lowest concentration values, which would meet validation criteria, signal-to-noise ratio, and accuracy on both Waters and Agilent HPLC systems. The system suitability results are summarized in Table 6. The validation parameters and test results for Acetaminophen Injection are summarized in Table 7. The example chromatograms of the Diluent, acetaminophen solutions, and some of the known impurities are presented in Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, and Figure 13.
| Parameter | Solution | Results |
|---|---|---|
Resolution Minimum resolution between any two components | System suitability solution | 3.05 between RC B and RC C (See Figure 10) |
Relative Retention Times 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | System suitability solution | 0.43 1.00 1.71 1.80 1.95 2.41 3.87 (See Figure 10) |
System Precision (RSD of 6 replicate injections) 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Sensitivity solution | 3.7% 1.1% 0.8% 0.8% 0.6% 1.5% 2.2% |
USP Signal-to-Noise Ratio 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Sensitivity solution | 73 67 77 68 102 40 78 (See Figure 11) |
| Parameter | Solutions | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Specificity (chromatographic separation) | Blank (Diluent), Standard solution, Sample solution, and spiked Sample solution | Any impurity peaks NLT 0.1% total area were separated from the main peak by a resolution of NLT 2.0, and from adjacent specified impurity peaks by a resolution of NLT 1.5. See Figure 9 for chromatogram of Blank. |
Limit of Quantitation (LOQ) 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Sensitivity solution and accuracy solution spiked with impurities at the LOQ level Experimentally determined by selecting the lowest concentration of analyte to meet validation signal-to-noise and recovery criterion (see also the Accuracy parameter of Table 7) | 0.03% or 0.3 μg/mL 0.03% or 0.3 μg/mL 0.03% or 0.3 μg/mL 0.03% or 0.3 μg/mL 0.03% or 0.3 μg/mL 0.05% or 0.5 μg/mL 0.05% or 0.5 μg/mL All concentration values meet a signal-to-noise criterion of NLT 10. All concentration values meet an average recovery of 100% ± 20% |
Linearity 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Linearity solutions: From LOQ to 1.0% of the nominal concentration of acetaminophen in the Sample solution (0.3 μg/mL of 4-aminophenol, acetaminophen, RC B, RC C, and Dimer or 0.5 μg/mL of RC D and RC J, and 1.5 μg/mL, 2.5 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL, 7.5 μg/mL, and 10 μg/mL for all compounds) | The correlation coefficients (r) of the linear curves for acetaminophen and impurities were NLT 0.99. The bias of the linear curves due to the intercept not being zero was NMT 2.0%. |
Accuracy 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Accuracy solutions: Acetaminophen sample solution (1.0 mg/mL) spiked at three levels compared to unspiked sample Unspiked (0%, n = 2) Spiked Sample solution at the LOQ level: 0.03% for 4-Aminophenol, RC B, RC C, and Dimer; and 0.05% for RC D and RC J (n = 6) Spiked Sample solution at 0.5% level: n = 3 Spiked Sample solution at 1.0% level: n = 3 | The average recovery for each specified impurity at each level were observed to be within: LOQ level: 100 ± 20.0% 0.5% level: 100 ± 10.0% 1.0% level: 100 ± 5.0 T he recovery calculations were calculated against the linearity data. |
Repeatability 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Repeatability solutions: 6 spiked Sample solutions at the LOQ level | The %RSD of the recovery was NMT 10.0% (n = 6) See Figure 12 for example chromatogram. |
Intermediate Precision 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Repeatability solutions: 6 spiked Sample solutions spiked at the LOQ level prepared and evaluated by a different analyst, on a different day by using different instrument and using a different serial numbered column | The average recovery for each specified impurity was observed to be 100 ± 20.0%. The %RSD of the recovery for each impurity was NMT 10.0% (n = 6) The %RSD for recoveries across the first and second analyst (n = 12) were NMT 15.0%. |
Solution Stability 4-Aminophenol Acetaminophen Acetaminophen RC B Acetaminophen RC C Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity Acetaminophen RC D Acetaminophen RC J | Sensitivity solution and spiked Sample solution freshly prepared at the LOQ level, stored at room temperature, and analyzed periodically over a 24-h period | Observed changes in the peak area from both solutions for each specified impurity and acetaminophen were within ± 10% of the initial time point values. |
| Sample Assay Test | Sample solutions | See Figure 13, Figure 14, and Figure 15 |
| Robustness | Robustness solution (0.1 mg/mL of acetaminophen and 0.01 mg/mL for all specified impurities) Changes evaluated:
| System suitability criteria for resolution, tailing factor, and relative retention time met across all evaluated conditions |
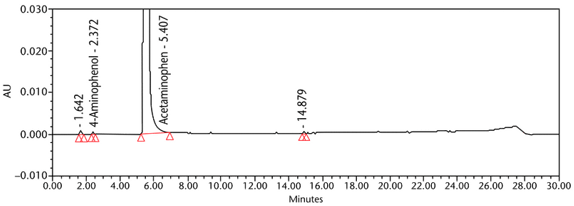
Determination of 4-Aminophenol
The Organic Impurities procedure described above is suitable to quantify 4-aminophenol. However, 4-Aminophenol can also be quantified using the procedure from the general chapter 4-Aminophenol in Acetaminophen-Containing Drug Products <227>3. Quantifications of 4-Aminophenol from three different sources of Acetaminophen Injection products were also performed following the procedure from <227>. The results are summarized in Table 8.
| Samples | <227> | Method Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | Not detected | Not detected |
| Sample 2 | Not detected | Not detected |
| Sample 3 | Not detected | Below LOQ |
![Figure 2f. N,N'-(6,6'-Dihydroxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3,3'-diyl)diacetamide (Acetaminophen Dimer Impurity)](/sites/default/files/inline-images/Figure%202f.%20N%2CN%27-%286%2C6%27-Dihydroxy-%5B1%2C1%27-biphenyl%5D-3%2C3%27-diyl%29diacetamide%20%28Acetaminophen%20Dimer%20Impurity%29_.png)
Comment On [Methods for the Analysis of Acetaminophen Injection]
Submitted on version:
Comment On [Methods for the Analysis of Acetaminophen Injection]
Submitted on version: